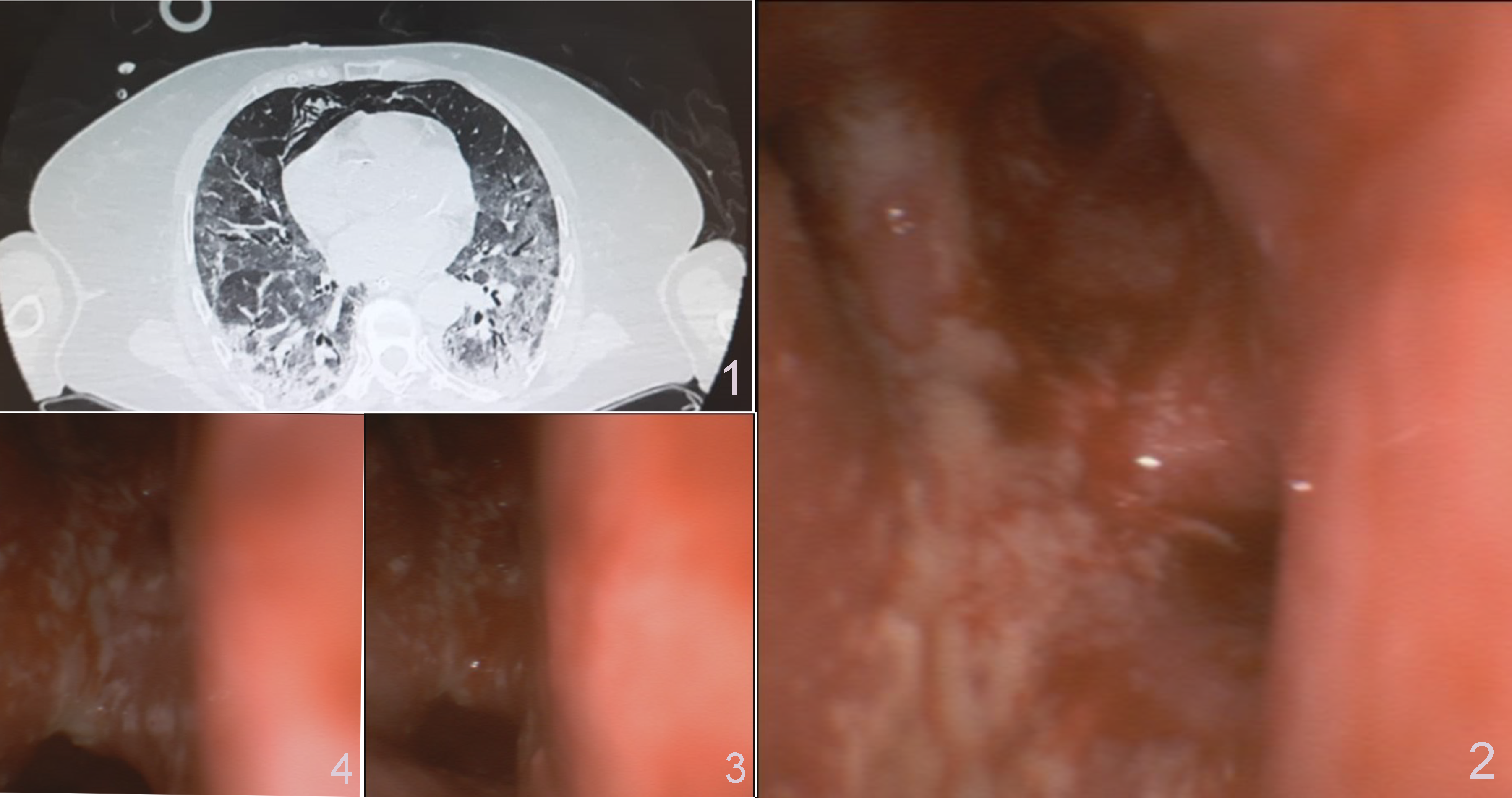
Bronchoscopy features of the newly described entity - COVID-19-associated pulmonary aspergillosis (CAPA)
Image Description
Recently, numerous reports signaled that patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) due to SARS-COV2 infection are more prone to develop secondary co-infections, such as invasive aspergillosis (1). Considering that patients with COVID-19 have none of the conventional risk factors for invasive aspergillosis, an additional burden in the management of these patients may occur (2).
We present a case of a 68-year-old female patient who was admitted to the intensive care unit (ICU) with severe ARDS secondary to COVID-19. She suffered from type 2 diabetes, hyperthyroidism, obesity, and coronary heart disease. Despite administering an antiviral treatment with Remdesivir, wide spectrum antibiotherapy, corticosteroids, and further anti-interleukin 6 therapy, the hypoxemic dysfunction persisted. On day 12 of admission increased bronchial secretion was observed, thus bronchial aspiration was ordered. Bronchoscopy evaluation revealed diffuse erythematous bronchial mucosa and a cavity with whitish, adherent pus on the bronchial wall. Aspergillus galactomannan Lateral Flow Assay and fungus cultures were performed confirming Aspergillus co-infection. Consequently, Isavuconazole treatment (200 mg q.d. after a loading dose of 200 mg t.i.d.) was rapidly initiated and a progressive respiratory improvement was registered. Seven days later, the patient was hemodynamically stable and a weaning trial from mechanical ventilation was planned. However, a sudden thromboembolic event led to obstructive shock causing the patient’s death on day 21.
References
Lai C-C, Yu W-L. COVID-19 associated with pulmonary aspergillosis: A literature review. J Microbiol Immunol Infect. 2021;54:46–53.
Koehler P, Cornely OA, Böttiger BW, Dusse F, Eichenauer DA, Fuchs F, et al. COVID-19 associated pulmonary aspergillosis. Mycoses. 2020;63(6):528–34.